Operationalizing the Machine Learning model inferencing with an engineering approach
What is a machine learning model inferencing?
Once you train a machine learning model to solve specific business problems, you need to think about how you would be consuming that model in production. The machine learning model inferencing is to generate the score and predict the output using the machine learning model. While the machine learning (ML) training environment is used to train the ML Model, the ML inference environment is where you operationalize your model to generate the score from your ML model.
Challenges faced in machine learning model inferencing
There are various challenges that require an engineering approach to come up with production-grade solutions, following is the brief on those challenges.
A plethora of Machine Learning Tools/Libraries/Frameworks
Data Scientists use various libraries like SKLearn, Keras, Pytorch, etc. to train machine learning models which in turn need different inferencing environments. If the ML model is trained using the SKLearn library then to generate score using that model requires the SKLearn runtime environment. The challenge here is about lock-in with one framework/tool ecosystem and it becomes difficult to create a common inference environment.
The requirement of different ML inferencing environments
The use cases of AI/ML have been wide-spread in various industries & domains having different requirements for ML model deployment and operations. The IIoT industry has a different demand to deploy the machine learning model because the ML model inferencing has to happen in a low configuration device or some time in embedded devices. Some use cases demand hosting models in the cloud environments with high scalability requirements while many use cases demand running inferencing environment on the edge server. The challenge here is that you need to prepare your runtime environment for such different targets by keeping in mind scalability and performance. The challenge is also about dependency on specific tools/libraries which were used to train the model because the runtime environment (i.e. embedded device) may not be able to support those tools and libraries.
Dynamic Scalability requirement in ML Inferencing
In certain situations, the ML model inferencing demands very high performance and scalability so the runtime environment must be capable of utilizing hardware acceleration or should be able to run in a low memory footprint. So preparing inference runtime with dynamic scalability and performance is another challenge, particularly to support various inference runtime targets mentioned in the above paragraph.
MLOps Pipeline Complexities
The model training and re-training pipeline builds the model and prepares all dependencies required during inferencing. In common scenarios, MLOps pipelines build docker images to package the ML model for inferencing, which increases complexities in image storage in the container registry along with the model stored in the model registry.
Operationalizing ML Models using ONNX
To overcome the challenges mentioned above, there needs to be a common ML inference environment without needing library/tool specific dependencies. To have such common inference runtime, there needs to be a common format for the machine learning model so that models trained using various libraries can be converted to a common format and can be used for scoring using common inference environment. There is such an open format for the machine learning model, which is called ONNX.
What is ONNX?
ONNX is an open format for machine learning models, it defines a common set of operators, file format so that ML models trained using different libraries can be converted to a common format.
What is ONNX Runtime?
The ONNX Runtime is an opensource inference runtime that understands ONNX formated ML model and provides model scoring runtime. It has a support for a variety of frameworks, operating systems and hardware platforms and built-in optimizations that deliver faster inferencing.
Proposed Architecture
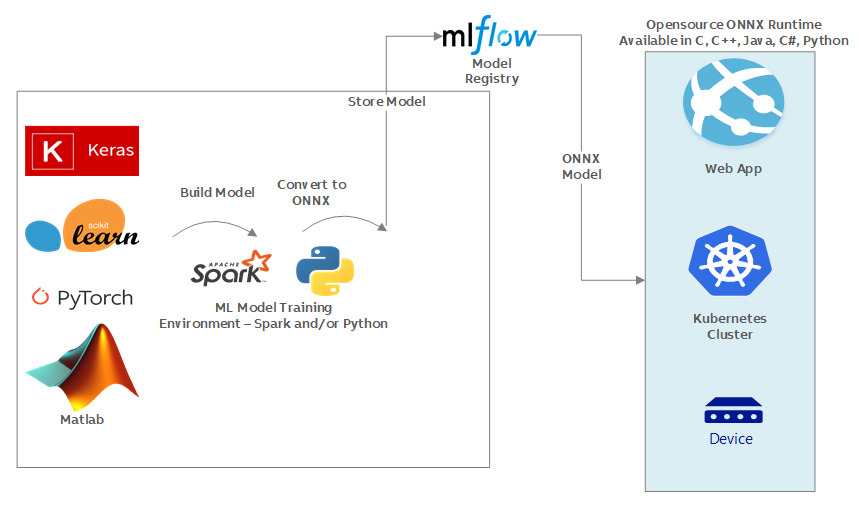
The proposed architecture recommends converting machine learning models trained using various libraries/frameworks into ONNX format. There are many open-source plug-ins available to convert models trained using Keras, SKLearn, Pytorch, Matlab etc. to common ONNX format so that only dependency for inference environment would be ONNX Runtime and nothing else. It helps Machine Learning engineers/Data Scientists to use the preferred framework without worrying about downstream inferencing implications. To manage the versioning of ML Models, it is recommended to use the model registry provided by another opensource component called MLFlow Model Registry. The core component in the proposed architecture is the ONNX inference runtime which is available in various languages targeting different technology platforms so that it can be plugged into existing technology stack. The MLFlow model registry needs to be integrated with ONNX Runtime such a way that runtime can load the ML Model from model registry based on inferencing request where the request can specify specific model and version to be used for inferenecing. The architecture does not cover security and access rights mechanism as it would be specific to enterprise AI strategy. The MLOps pipelines can train the model, convert the model into ONNX format, and then store it to MLFlow model registry with specific version information. With this architecture approach, lots of complexities go away from MLOps pipelines as we are not building any docker images, not preparing any conda environment for dependencies, or not worrying about the target inferencing environment. The availability of ONNX Inference Runtime in various language platforms helps operationalize the same models in different hardware and software requirements.
There is a need to bring in many more such engineering approaches to operationalize ML/AI and make enterprise AI successful.