Hands-on with blockchain - Hyperledger Fabric Part-I
About this article
This is the first part of the HyperLedger Fabric Hands-on where I am going to cover brief introduction of HyperLedger Fabric and setting-up the system to start first blockchain network and test out first-network. The hands-on on development of actual DApp (De-centralized Application) would be covered in next part of the post.
What is Hyperledger?
The Hyperledger is a an umbrella project started by Linux Foundation for open source Blockchains and tools.
What is Hyperledger Fabric then?
Hyperledger Fabric is one of the umbrella projects of Hyperledger and it has been one of the most successful Blockchain projects. It has been developed with advanced architecture principles which includes pluggable modules, scalable, secure and it’s unique differentiation - permissioned. The source code is written in Go language and there are SDKs available in various languages like NodeJS, Python, Go. It is a micro-service architecture and uses docker containers to host various modules.
The Hyperledger Fabric is private and permissioned (it is not like Ethereum in which any unknown identities can take part in network and uses ‘proof of work’ protocol). In Hyperledger Fabric, members can only join through trusted Membership Service Providers. Although Hyperledger Fabric is permissioned network, the network can be established across industries and businesses to execute different types of contracts.
Why Blockchain?
To understand the needs of Blockchain network, one needs to understand how different types of transactions take place in current digital age and how it worked in past(before digitization). It can be explained well with example, let us take one buyer and one supplier hypothetical example. The buyer wants to buy some asset from supplier and now if we consider this transaction before digital age, they will agree upon some terms/contract to carry out this transaction. Usually there could be a broker also who could be trusted by both parties so that whatever transaction records maintained by both parties can be validated and broker will approve the transaction and charge some commission for the same purpose. Also there is a chance of loss in records maintained by one of the parties and in that case both parties must agree upon whatever records maintained by another party. The digital age brought only technology revolution and not in terms of how these transactions are carried out. With digital technologies, we could just digitize the records in ledger or may be centralize those records but still we need to rely on central authority to approve the transactions (e.g. Reserve Bank in money transaction). Once we maintain records in central place (like SSN in USA, Aadhaar in India) , there is a chance of someone stealing the records, update it and we will always have to trust the central authority.
To make sure that there is no central authority and transactions are decentralized (stored on multiple machines - peers), we need to make sure that trust is established by multiple peers for all transactions carried out. If buyer is buying some assets from supplier, the transaction record would be available with all peers and nobody would be able to modify the transaction as it would be always append-only. The transaction must be approved by all peers and it would be carried out as per the contract. Basically Blockchain provides us all of these and much more, also there are many use-cases in current world could be benefited with de-centralized blockchain technology (e.g. Youtube kind of Video Streaming, Banking transactions, Public E-Mail providers, Property record registries, Identity Management and many more).
How Hyperledger Fabric works?
The Hyperledger Fabric has a modular design, which provides freedom to network designer to select various algorithms, choice in ledger storage, choice in consensus and encryption techniques. Following is a brief on various functionalities available in Hyperledger Fabric. These are explained very briefly below, it would be discussed in detail in next hands-on post as focus of this post is to start private network locally and verify if network is correctly running with all modules.
Assets
Assets can be anything on which transaction can be carried out. It can be some kind of contract or some kind of hardware assets. The Hyperledger Fabric provides Chaincode/Smart Contract to modify the assets.
Ledger
There are two components in Hyperledger Fabric Ledger, one is World State and another is transaction logs. The world state is where the current state of transaction is maintained and history is maintained in transaction logs. The world state is read-only and can be queried using SDK while transaction logs cannot be modified but new transaction can be added into it. Due to modular design, data storage for world state is pluggable (you can use your own storage, the default database is LevelDB).
Smart Contract
In Hyperledger Fabric, the smart contract is chaincode. It can be executed by any application outside of blockchain and usually it interacts with World state part of the ledger and not the transactions. The smart contract is the executable code, which can be used by application to query the data or execute new transaction.
Consensus
The order of transaction is very important in blockchain, transactions must be written to ledger in order in which they occur. There must be a way to reject a bad or malicious transaction and to do that there is a need of consensus mechanism so that policy can be established to accept the transaction based on how many peer nodes have approved the transaction. The Hyperledger Fabric provides flexible consensus mechanism using which network starters can define their mechanism for consensus. On other hand the Ethereum uses proof of work to mine the blockchain block, which can be done only by executing complex cryptographic algorithms (it requires lot of computing power) - whichever miner mines the block first will get priority and consensus is established. The Hyperledger Fabric uses Apache Kafka and Apache Zookeeper as a technology to order the transactions.
Privacy
In Hyperledger Fabric, organization can be a member and privacy can be established by creating a Channel withing organization. The channel will have its own ledger and can only be shared with members of that channel. The network can have multiple channels and participant can be part of more than one channel. The participant will have ledger copy for each channel where it is a member so participant cannot access ledger belonging to another channel where it is not a member.
Identity Management & Security
All participants in network have known identity, which is managed by Membership Service Providers (MSPs). The MSP uses Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) to establish identities and per channel MSP makes sure tha member is identified by MSP allocated to channel.
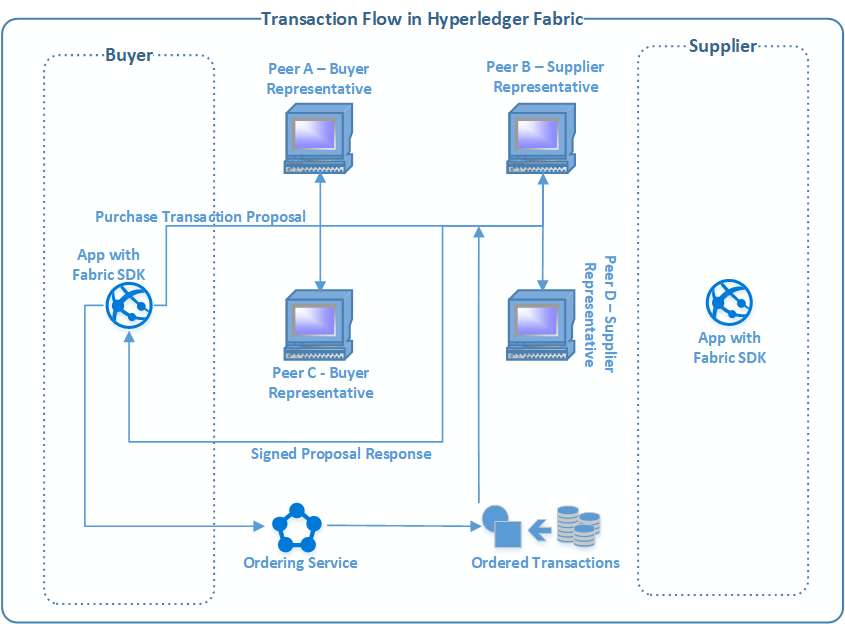
How transaction takes place in Hyperledger Fabric?
In above transaction flow buyer wants to buy some asset from supplier and it is explained below how the entire transaction will take place in Hyperledger Fabric network. It is assumed that both Buyer and Supplier are registered on network, they hve dedicated channel created and cryptographic certificates provided to interact with Membership Service provider.
The buyer is sending purchase request using SDK, which targets Peer A, Peer B, Peer C & Peer D as they all supposed to endorse the transaction as per the endorsing policy defined. The endorsement policy can be defined by members of the network based on types of transaction. The request is going to execute Chaincode (Smart Contract) residing on peers, all peers will validate the transaction by looking at the the format, duplication, signature validation (through MSP), channel authorization (whether the buyer is authorized to execute the chaincode). If all is good then the transaction proposal inputs would be used as a parameters in chincode function residing on peer and function would be executed. The chaincode would be executed against world state database and response would be prepared with read/write result. It is important to note here is that ledger is still not updated(which will happen later), the proposal response would be signed by endorsing peers and response would be sent back to buyer app. The buyer app will verify the response by looking at endorsing peer’s signature and consume the data if it was only read request. If it was write request then application will validate the endorsing policy (whether all required peers have endorsed the transaction) and broadcasts the proposal request and response to ordering service. The ordering service inspects the transaction and orders them per channel and creates the transaction block. These transactions then delivered to all peers and validated, the validated transactions are then updated to ledger by all peers. If there are any write sets in proposal response then they would be committed to state database.
Setting-up your system for Hyperledger Fabric
The operating system used here to setup Hyperledger Fabric is Ubuntu 16.04 LTS, following steps need to be followed to run first network in your system.
- Install Git client
- Install go using following command
sudo apt install golang-go
You will also need to set GOPATH permanently as instructed here - Install Docker
- Install docker-compose and follow the instructions in linux tab
- Install pip - follow the instructions for Ubuntu/Debian
- pip install –upgrade pip
- Install python By default Ubuntu 16.04 comes with Python 3.5.1 installed as the python3 binary. The Fabric Node.js SDK requires an iteration of Python 2.7 in order for npm install operations to complete successfully. Retrieve the 2.7 version with the following command: sudo apt-get install python verify the version with command: python –version
- Install Nodejs 8.9.x (As of now you must need 8.9.x version)
sudo apt-get install curl
curl -sL https://deb.nodesource.com/setup_8.x | sudo -E bash -
sudo apt-get install -y nodejs
sudo npm install npm --global
You may need to set default node version if you have multiple versions of nodejs installed To change default node version (you may need to install nvm if not installed already) nvm alias default 8.11.3 (to view all versions of node, use ‘nvm ls’)
- Download all fabric images & fabric sample
curl -sSL http://bit.ly/2ysbOFE | bash -s 1.2.0 Running your first Hyperledger Fabric network
We will start our first network from sample but before you run your first sample, Install everything you need to run first network including fabric images.
sudo bash fabric-samples/scripts/bootstrap.shRun first-network by navigating to first-network folder in fabric-samples directory
./byfn generate(generates certificate, genesis block and other artifacts. The artifacts can be found in first-network/channel-artifacts folder)
./byfn up(start your first network)
./byfn down(shutdown your first network)
You should be able to see ‘All GOOD, BYFN execution completed’ message if all went well. This post is the foundation for next post where we will create sample DApp (De-centralized Application) and use SDK to interact with network.